Learning Genetics Can Be Fun - Solutions
1. Two black dogs could be homozygous black (BB) or heterozygous black (Bb). Yellow must be homozygous, therefore cannot be the same genotype as black.
2. P Cc x Cc
F1 CC, Cc, Cc, cc both parents are normal but “carry” the allele for CF. One in four children will inherit it.
3. a) P Rr x rr
b) R, r and r, r
F1 Rr, Rr, rr, rr 1 round:1 wrinkled
F2 RR, Rr, Rr, rr 3 round:1 wrinkled
4. P Ll x ll
F1 Ll, Ll, ll, ll 1 long:1 short
5. P T_ x tt
F1 327 tall: 321 short - almost 1:1 therefore unknown parent must be heterozygous. Note: homozygous (LL) would give ALL tall plants in F1.
6. The presence of all smooth in the offspring means smooth is dominant.
P SS x ss
F1 Ss
F2 3:1
7. a) P Ss x Ss
F1 SS, Ss, Ss, ss
b) P S_ x _ _
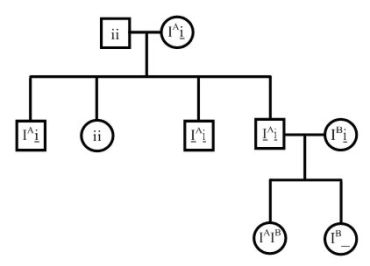
The female must be heterozygous as she produced non-spotted pups. The unknown male must be homozygous recessive (ss). If he were homozygous dominant, all pups would be spotted. If he were heterozygous, you would expect a 3:1 ratio in pups.
8. (i) P T_ x tt The male must be heterozygous (Tt) to be able to produce
F1 tt both trotters and pacers. If he were homozygous dominant
(ii) P T_ x tt her would produce only trotters.
F1 Tt
(iii) P T_ x Tt
F1 tt
9. Normal woman Pp (must be heterozygous because father was albino)
Husband pp
Husband’s parents both Pp
Children Pp, Pp, pp
10. test cross W_ x ww
11. P Pp x Pp
F1 PP, Pp, Pp, pp chance of PKU is 1/4
12. P Bb x Bb
F1 BB, Bb, Bb, bb
a) 1/4 (b) 1/4 (c) 1/2
d) 1 homozygous brown:2 heterozygous brown:1 homozygous blonde
e) 3 brown:1 blonde
f) not possible because blonde (b) is recessive
g) C = curly; c = straight
h) P Cc x cc
F1 Cc, Cc, cc, cc
i) C, c (j) c, c (k) 0 (l) 1/2 (m) 1/2
n) 1 heterozygous:1 homozygous recessive
o) 1 curly:1 straight
p) No. Straight hair is recessive so individual MUST be homozygous (cc).
13. B - black; b - white; S - short; s - long
a) P BBSs x bbss
F1 BbSs, Bbss 1 black, short:1 black, long
b) P BbSs x bbss
F1 BbSs, Bbss, bbSs, bbss 1 black, short:1 black, long: 1 white, short:1 white, long
c) P BBss x BbSs
F1 BBSs, BBss, BbSs, Bbss 1 black, short:1 black, long
d) i) (a) 1/2 (b) 1/4 (c) 1/2
ii) (a) 1/2 (b) 1/4 (c) 1/2
iii) (a) 0 (b) 1/4 (c) 0
14. B - black; b - white; S - solid; s- spotted
male female
a) P B_S_ bbS_
F1 2 BbS_ , 2 bbS_
Some white pups so the male must be Bb. The absence of any non-spotted pups suggests that female A is SS but we can’t say for sure.
b) P BbSs B_S_
F1 bbss
the presence of white, non-spotted pups means that female B must be BbSs
c) P BbSs bbss
F1 bbSs , bbss , BbSs , Bbss
The genotype of female C can be determined from her phenotype.
15. SR - round; SL - long
P SRSL x SRSL
F2 SRSR, SRSL, SRSL, SLSL (incomplete dominance)
16. P SNSM x SNSM
F1 SNSN, SNSM SNSM, SMSM 25% chance of having homozygous recessive child
17. CRCR - chestnut; CMCM - cremello; CMCR - palomino
P CMCR x CMCM
F1 CMCM, CRCM 1 cremello:1 palomino
18. P FRFW x FRFW
F1 FRFR, FRFW, FRFW, FWFW
a) ½ pink
b) 1/4 red
c) 1/4 white
d) 1:2:1
e) 1:2:1
19. woman IB_ x man IA_
F1 ii is possible if mother and father were both heterozygous. The facts are inconclusive.
20. P ♂ ii x ♀ IAIB
F1 IAi, IBi
AB ♀ could produce AB offspring if ♂ were type A, B, or AB; she could never produce type O in F1 because she always donates either A or B.
21. a) P ChCa x CaCa
F1 ChCa, CaCa 1 himalayan:1 albino
b) P CCa x CchCa
F1 2 C_, Cch_, CaCa
c) P CchCch x CchCa
F1 CchCch, CchCa 1 chinchilla:1 light gray
d) P CchCh x CaCa test cross
F1 5 ChCa, 5 CchCa
22. note: cc = no purple
P Ppcc x PPCc
gametes Pc, pc PC, Pc
F1 PPCc, PPcc, PpCc, Ppcc
phenotypes 1 purple, curved: 1 white, straight: 1 purple, curved: 1 white, straight (1:1)
23. a) P CCBB (black) x Ccbb (brown)
F1 CCBb (black), CcBb (black)
b) P ccBB (albino) x CcBb (black)
F1 CcBB (black), CcBb (black), ccBB (albino), ccBb (albino)
c) P CcBb (black) x ccbb (albino)
F1 CcBb (black), Ccbb (brown), ccBb (albino), ccbb (albino)
d) P CcBb (black) x CcBb (black)
F1 CCBB (black), CCBb (black), CcBB (black), CCbb (brown), CcBb (black), Ccbb (brown), ccBB (albino), ccBb (albino), ccbb (albino)
note: you would get the normal 9:3:3:1 as in any heterozygous dihybrid cross but ccBB, ccBb, and ccbb all combine to give 4 albino (a bit tricky, eh?)
24. a) 4 children
b) A is Dd, B is Dd
c) M is dd, N is dd
25.
